Labor market activity has been gradually recovering for the second consecutive quarter. After a sharp improvement mid-year, positive momentum continued in the third quarter, with growth observed in both employment and overall economic activity of the population.
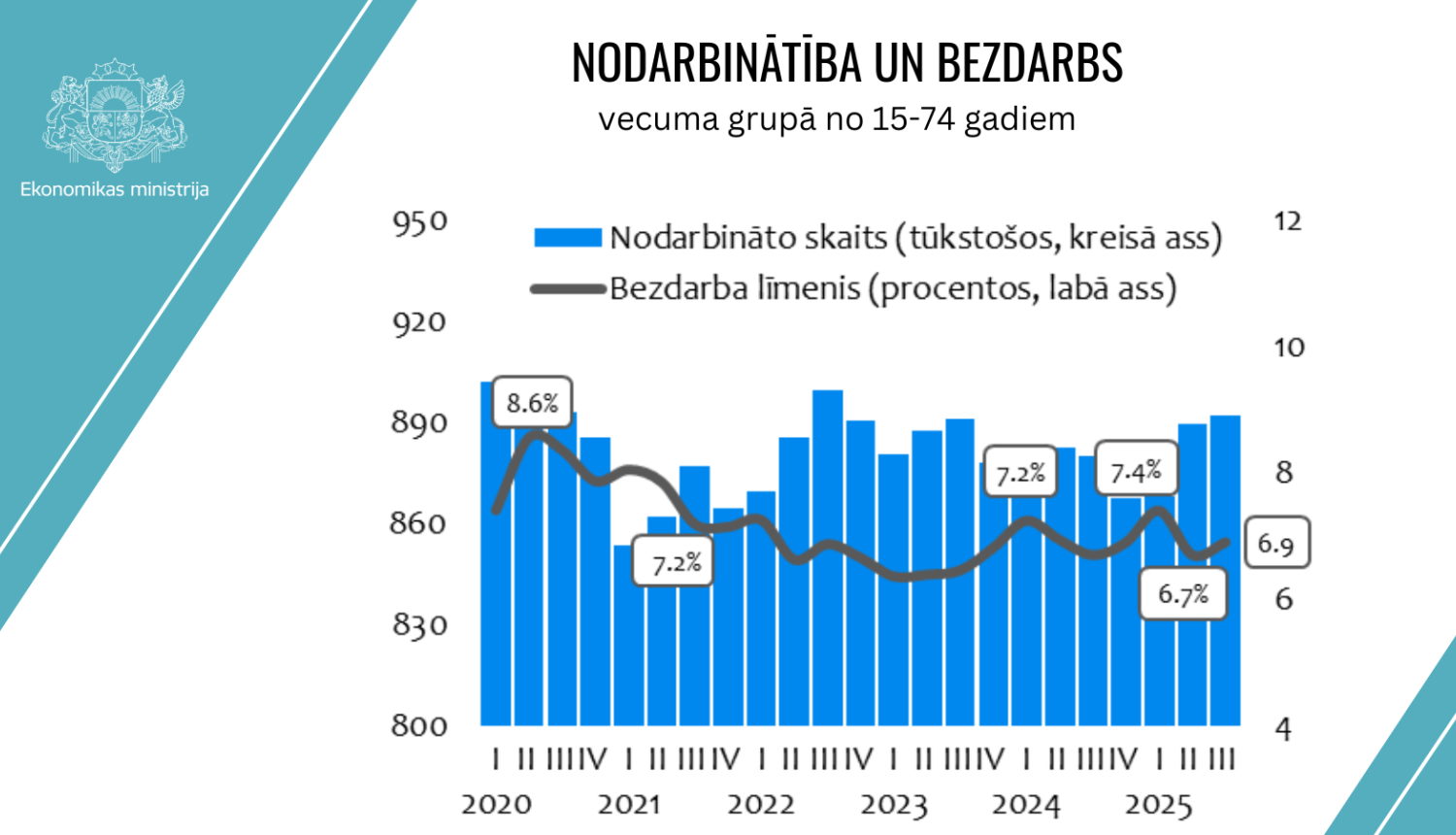
According to data from the Central Statistical Bureau’s labor force survey, the number of employed persons increased by 1.4% (12,000 people) in the third quarter of 2025 compared to the third quarter of 2024, marking the fastest annual growth since the end of 2022.
Compared to the second quarter of 2025, the number of employed rose by 2,700 people, or 0.3%.
The employment rate reached 65.2% in the third quarter, up 0.3 percentage points from the previous quarter. Compared to the third quarter of 2024, the employment rate increased by 1 percentage point.
The unemployment rate rose to 6.9% in the third quarter of 2025, up 0.2 percentage points from both the second quarter of 2025 (6.7%) and the third quarter of 2024 (6.7%). At the same time, the unemployment rate remained 0.5 percentage points below the first quarter of 2025 (7.4%). Overall, the number of unemployed reached 66,200 people aged 15–74, an increase of 2,500 compared to the previous quarter. The slight rise in unemployment is mainly explained by higher economic activity and an increase in overall labor supply.
Economic activity among the population continued to rise in the third quarter of 2025. The activity rate reached 70%, up 1.2 percentage points from the third quarter of 2024 (68.8%) and 0.4 percentage points from the second quarter of 2025 (69.6%). Economic activity is approaching 2020 levels, the highest in the past five years. In the third quarter of 2025, the number of economically active individuals aged 15–74 reached 958,300, an increase of 15,200 compared to the same quarter in 2024 (943,100).
Despite continued economic uncertainty, the labor market in Latvia remained stable in the third quarter of 2025. Following significant improvements in the second quarter, both employment and economic activity continued to rise in the third quarter, indicating overall labor market resilience. Although a slight increase in unemployment was observed, this was largely due to supply-side factors and rising economic activity. The number of long-term unemployed also increased, partially pointing to a rise in structural unemployment, meaning that despite growing labor supply, risks of labor shortages remain relevant.
It is expected that the labor market will maintain positive trends through the end of the year, though a significant increase in labor demand in the final quarter is unlikely. Overall, employment in 2025 is expected to rise by around 0.3% (approximately 3,000 people) compared to 2024, while the unemployment rate may fall to 6.7%.